Table of Contents
ToggleThe healthcare industry stands at the threshold of a digital revolution, where interoperability in healthcare is not just a buzzword but a critical enabler of better patient outcomes and operational efficiency. As healthcare ecosystems grow more complex, the ability of disparate systems to communicate seamlessly is transforming care delivery, empowering providers, and enhancing patient experiences.
Interoperability is the bridge that connects Electronic Health Records (EHRs), patient management systems, and advanced analytics platforms. By ensuring these systems talk to each other, healthcare organizations can unlock the full potential of data-driven healthcare to support better decision-making, improve collaboration, and adapt to patient-centric care models. In recent years, digital transformation in healthcare has accelerated, with interoperable systems playing a key role in reshaping the industry.
For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, organizations that invested in interoperability were able to share patient data rapidly, coordinate care across facilities, and leverage real-time analytics to manage resources effectively. This demonstrated the power of connected systems in tackling global healthcare challenges.
What is Interoperability in Healthcare?
Interoperability in healthcare refers to the ability of various healthcare systems, applications, and devices to exchange and interpret data seamlessly. It ensures that patient information flows smoothly between different stakeholders like hospitals, clinics, pharmacies, labs, and insurers, creating a unified ecosystem that promotes better decision-making and enhances care delivery. 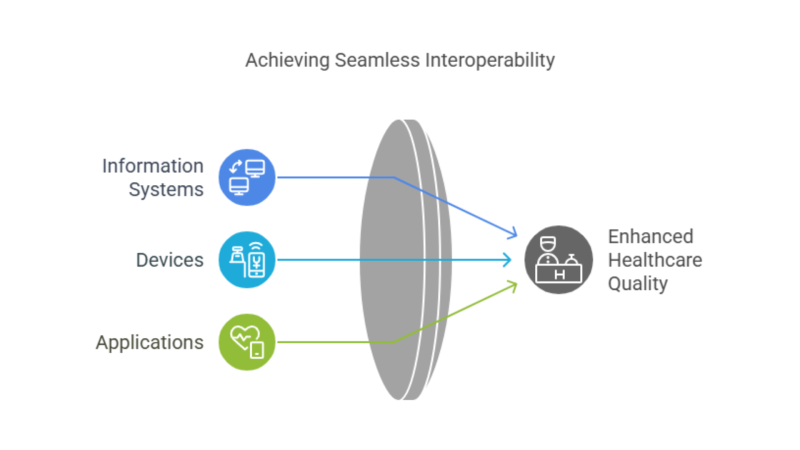 At its core, interoperability eliminates data silos by enabling systems to “speak the same language.” For instance, a patient’s electronic health record (EHR) created at one hospital should be accessible and interpretable at another, ensuring continuity of care regardless of location or provider.
At its core, interoperability eliminates data silos by enabling systems to “speak the same language.” For instance, a patient’s electronic health record (EHR) created at one hospital should be accessible and interpretable at another, ensuring continuity of care regardless of location or provider.
Types of Interoperability in Healthcare
- Foundational Interoperability: The basic ability of one system to exchange data with another. For example, a laboratory sending a test result in a format readable by a hospital’s system.
- Structural Interoperability: Focuses on the data format and organization, ensuring that data exchanges are consistent and interpretable.
- Semantic Interoperability: The most advanced form, ensuring that systems not only share data but also understand its context.
- Organizational Interoperability: Addresses governance and legal frameworks to ensure that systems collaborate efficiently across different entities.
Interoperability forms the backbone of digital transformation in healthcare. It enables the seamless integration of innovative solutions like telehealth, AI-driven diagnostics, predictive healthcare models, and personalized medicine. For example:
- A connected healthcare ecosystem allows a diabetic patient to share glucose monitor readings with their doctor in real-time, enabling timely interventions.
- It supports population health management by aggregating data from diverse sources for insights into disease trends and prevention strategies.
By promoting data-driven healthcare, interoperability empowers providers to focus on patient-centric care, reducing administrative burdens and ensuring data accessibility when it matters the most.
The Importance of Interoperability in Healthcare
Interoperability plays a pivotal role in modernizing healthcare systems and driving innovation. In an industry heavily reliant on accurate, timely information, the seamless exchange of data between disparate systems ensures a comprehensive, coordinated approach to patient care. Here are several reasons why interoperability in healthcare is so critical:
Improved Patient Care and Safety
With interoperability, healthcare providers can access comprehensive patient records across systems, ensuring that all involved parties have up-to-date information. This reduces the risk of medical errors caused by incomplete or missing data, such as prescribing incorrect medications due to a lack of knowledge about existing prescriptions.
For example, if a patient moves between healthcare providers or is treated in multiple hospitals, their medical history, lab reports, and treatment must follow them, making care more accurate and timely.
Enhanced Collaboration Across Providers
When healthcare professionals have access to the same data, it fosters better communication between various departments and care teams. This is particularly crucial in managing patients with complex conditions that require the expertise of multiple specialists. With interoperable systems, doctors, nurses, and allied health professionals can easily share information and collaborate on treatment plans, resulting in more holistic patient care.
Support for Digital Transformation and Innovation
As healthcare systems continue to evolve, interoperability forms the foundation of innovation in fields like telemedicine, AI, and predictive analytics. Without a seamless flow of data, innovations in digital healthcare solutions cannot function effectively.
For example, telemedicine platforms rely on interoperable systems to ensure that real-time data from wearable devices, patient records, and remote consultations all come together in one cohesive system, enabling personalized care from a distance.
Regulatory Compliance and Reporting
The shift toward value-based care and regulatory changes, such as the implementation of the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act, has put increased pressure on healthcare organizations to comply with standards for data exchange. Interoperable systems make it easier to meet these regulations and report data efficiently, ensuring that organizations maintain compliance while reducing administrative burdens.
The Era of Data-Driven Healthcare
Interoperability in healthcare isn’t just about exchanging data. It’s about ensuring that data flows in a standardized, secure, and accessible manner, allowing healthcare providers to leverage advanced tools like data analytics, predictive analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) for improved decision-making and patient care.
Data Analytics in Healthcare Interoperability
Interoperability makes data more accessible and usable. By connecting disparate systems, such as electronic health records (EHRs), laboratory systems, and imaging platforms, healthcare providers can analyze data in real-time. This allows for a more comprehensive understanding of patient health, trends across populations, and even operational efficiencies. Data analytics can help identify health patterns, streamline workflows, and improve clinical decisions.
For example, hospitals that employ interoperable systems can analyze patient data across multiple departments to detect early signs of chronic conditions, such as diabetes or heart disease. With this data, doctors can develop more personalized treatment plans, improving patient outcomes.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics is a powerful tool enabled by interoperability. By integrating patient data from multiple sources (e.g., EHRs, wearable devices, diagnostic tools), healthcare systems can generate predictions about future health events. Predictive models can forecast a range of outcomes, from disease progression to hospital readmission risk. An interoperable healthcare data system supports the collection of vast amounts of data needed for predictive models.
For instance, predictive analytics can be used to assess the likelihood of a patient being readmitted to the hospital based on their medical history, medication adherence, and other factors. This enables providers to intervene earlier and reduce preventable readmissions.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML)
AI is transforming healthcare by providing deep insights through machine learning (ML) models, which require vast datasets to train and refine. Interoperable systems make it possible for AI models to access data across different systems and healthcare providers, leading to more accurate diagnoses, tailored treatment plans, and even new treatments.
For instance, AI tools that analyze medical imaging rely on interoperable systems to access patients’ complete medical history, including previous imaging results, diagnoses, and lab reports. This allows the AI to detect anomalies and offer recommendations more accurately than human clinicians alone.
Challenges in Achieving Interoperability
While interoperability in healthcare offers numerous benefits, it is also accompanied by several challenges that can hinder successful implementation. These challenges need to be addressed to fully realize the potential of data-sharing across healthcare systems.
1. Data Privacy and Security Concerns
One of the most significant obstacles to achieving interoperability in healthcare is the concern about patient data privacy and security. With the increasing number of healthcare data breaches and cyber threats, healthcare organizations are wary of sharing sensitive patient information across different platforms. Data protection regulations, such as HIPAA in the United States, also create strict guidelines limiting how patient information is shared.
2. Lack of Standardization
The lack of common data standards is another major hurdle in achieving interoperability. Healthcare systems, applications, and devices use different formats, terminologies, and protocols, making sharing data seamlessly between them difficult. The absence of uniform data standards results in data fragmentation, which ultimately leads to inefficiencies and data silos.
3. High Implementation Costs
Implementing interoperable systems can be expensive, particularly for smaller healthcare providers. These systems often require significant investment in technology, training, and process reengineering, which may be beyond the reach of many organizations. Furthermore, there is a lack of clear ROI (Return on Investment) metrics for interoperability, making it difficult for healthcare organizations to justify the initial financial outlay.
4. Resistance to Change
Healthcare providers and staff are often resistant to adopting new technologies and processes. Change management in healthcare is a slow and complicated process, with many professionals preferring traditional, familiar workflows. The fear of disrupted routines, additional training requirements, and potential challenges in system integration often cause delays in adopting interoperable systems.
How Netwin Overcomes Challenges
Netwin understands that achieving interoperability in healthcare comes with its own set of challenges. Here’s how we address these barriers to create seamless and efficient interoperable systems for our clients:
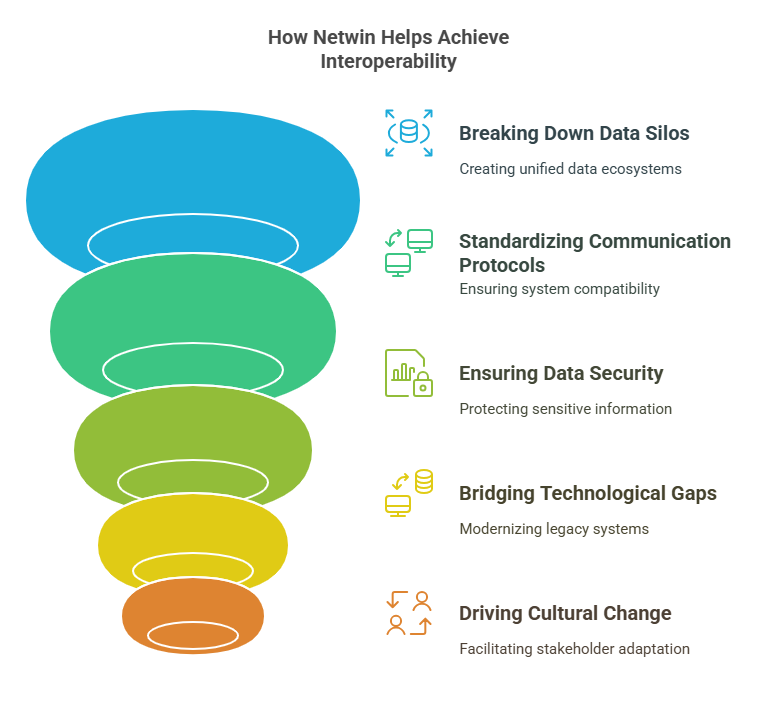
Breaking Down Data Silos
One of the biggest challenges in interoperability is data silos caused by disconnected systems. Netwin’s tailored solutions utilize advanced cloud platforms like AWS and Microsoft Azure to create unified healthcare data ecosystems. These platforms enable secure storage and centralized access to data, ensuring all stakeholders like clinicians, patients, and administrators have access to the same accurate information in real-time.
Standardizing Communication Protocols
Disparate healthcare systems often use different data formats and protocols, creating integration roadblocks. Netwin leverages industry-standard APIs and data formats like FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) and HL7 to ensure compatibility between systems. By implementing these standards, Netwin fosters smooth data exchange and ensures compliance with global healthcare regulations.
Data Privacy and Security
With healthcare data being highly sensitive, ensuring its security is critical. Netwin adopts cutting-edge encryption techniques, multi-layered authentication, and compliance with regulatory standards like HIPAA and GDPR. These measures safeguard data while enabling trusted sharing across systems.
Bridging Technological Gaps
Legacy systems are often incompatible with modern healthcare IT solutions. Netwin specializes in modernizing legacy systems by integrating them with next-generation tools and technologies. Our approach ensures that healthcare organizations can continue using existing infrastructure while enabling interoperability.
Driving Cultural and Organizational Change
Resistance to change is a common barrier when implementing interoperable systems. Netwin collaborates closely with healthcare stakeholders, offering comprehensive training programs and change management strategies. These initiatives empower healthcare professionals to adapt to new systems confidently and seamlessly.
Custom Solutions for Complex Challenges
Every healthcare organization has unique interoperability requirements. Netwin conducts in-depth assessments to identify specific pain points and then develops tailored solutions to address these challenges. From integrating Electronic Health Records (EHRs) to enabling advanced data analytics, Netwin ensures every solution aligns with the organization’s needs and goals.
By leveraging robust technology, adhering to global standards, and addressing both technical and cultural barriers, Netwin enables healthcare organizations to achieve true interoperability. This commitment ensures better patient outcomes, improved operational efficiency, and future-ready healthcare systems.
Benefits of Interoperable Systems in Healthcare
Interoperable systems are transforming the healthcare sector by improving care delivery, streamlining operations, and enhancing overall patient experience. Here are the key benefits of adopting interoperability in healthcare systems:
Improved Patient Care and Safety
A study by the American Hospital Association found that interoperability reduces medication errors by allowing healthcare professionals to view a patient’s full prescription history across providers, ensuring better prescribing practices.
Interoperability enables healthcare providers to access comprehensive patient data from multiple sources, including medical history, lab results, and medication records. This access ensures clinicians can make informed decisions, reduce errors, and avoid duplication of tests, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Enhanced Efficiency and Reduced Operational Costs
With interoperable systems, healthcare providers can streamline workflows by automating data entry, reducing administrative burden, and improving coordination across different departments and care teams. This leads to significant cost savings by eliminating redundant tasks and optimizing resource allocation.
The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that electronic health records (EHRs), enabled by interoperability, can help reduce the administrative costs of managing patient data by up to 30%, especially when integrated with billing, scheduling, and other healthcare management systems.
Empowered Patients and Improved Patient Experience
Interoperable systems allow patients to access their own health records across multiple platforms, giving them greater control over their healthcare journey. This promotes patient engagement and enables better self-management of chronic conditions.
The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) highlighted that when patients have access to their electronic health information, they are more likely to follow treatment protocols, improving adherence rates and health outcomes.
Better Collaboration Across Healthcare Teams
Healthcare professionals can collaborate more effectively when they have access to a shared pool of patient data. This fosters better communication between specialists, primary care providers, and hospitals, ensuring a more coordinated approach to treatment.
Streamlined Compliance and Reporting
Interoperability helps healthcare organizations meet regulatory requirements by making it easier to manage and report patient data. This is especially crucial for adhering to policies like the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act and the Affordable Care Act.
Facilitation of Data-Driven Healthcare
Research published in Health Affairs indicates that when patient data from multiple sources is integrated, predictive models can be used to identify high-risk patients and prevent hospital readmissions, saving millions in healthcare costs.
Interoperability unlocks the power of data analytics by enabling the aggregation and analysis of data from various healthcare systems. This allows healthcare providers to identify trends, predict patient outcomes, and optimize treatment plans.
Supports Value-Based Care Models
Interoperable systems bring transformative benefits to healthcare, enabling better patient outcomes, improved efficiency, and a more data-driven approach to care. By streamlining communication, enhancing collaboration, and ensuring seamless data exchange, these systems are a vital component of the modern healthcare landscape, supporting both clinical decision-making and operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Interoperability in healthcare is no longer a futuristic ambition but a pressing necessity in the age of data-driven healthcare and digital transformation. By enabling seamless communication between systems, healthcare providers can deliver personalized care, improve operational efficiency, and drive innovation. However, achieving true interoperability requires overcoming significant challenges such as data silos, differing standards, and resistance to change.
The benefits far outweigh these challenges, with advancements in predictive analytics, AI, and data-sharing ecosystems paving the way for more effective and efficient healthcare delivery. Netwin is at the forefront of this transformation, offering tailored solutions that empower healthcare organizations to harness the full potential of interoperable systems.
As the healthcare industry continues its shift toward patient-centered care, decision-makers must embrace interoperability as the cornerstone of modern healthcare IT. The journey may be complex, but with the right technology partners and a clear vision, it is a journey that promises a healthier future for all.